Menstrual Disorders
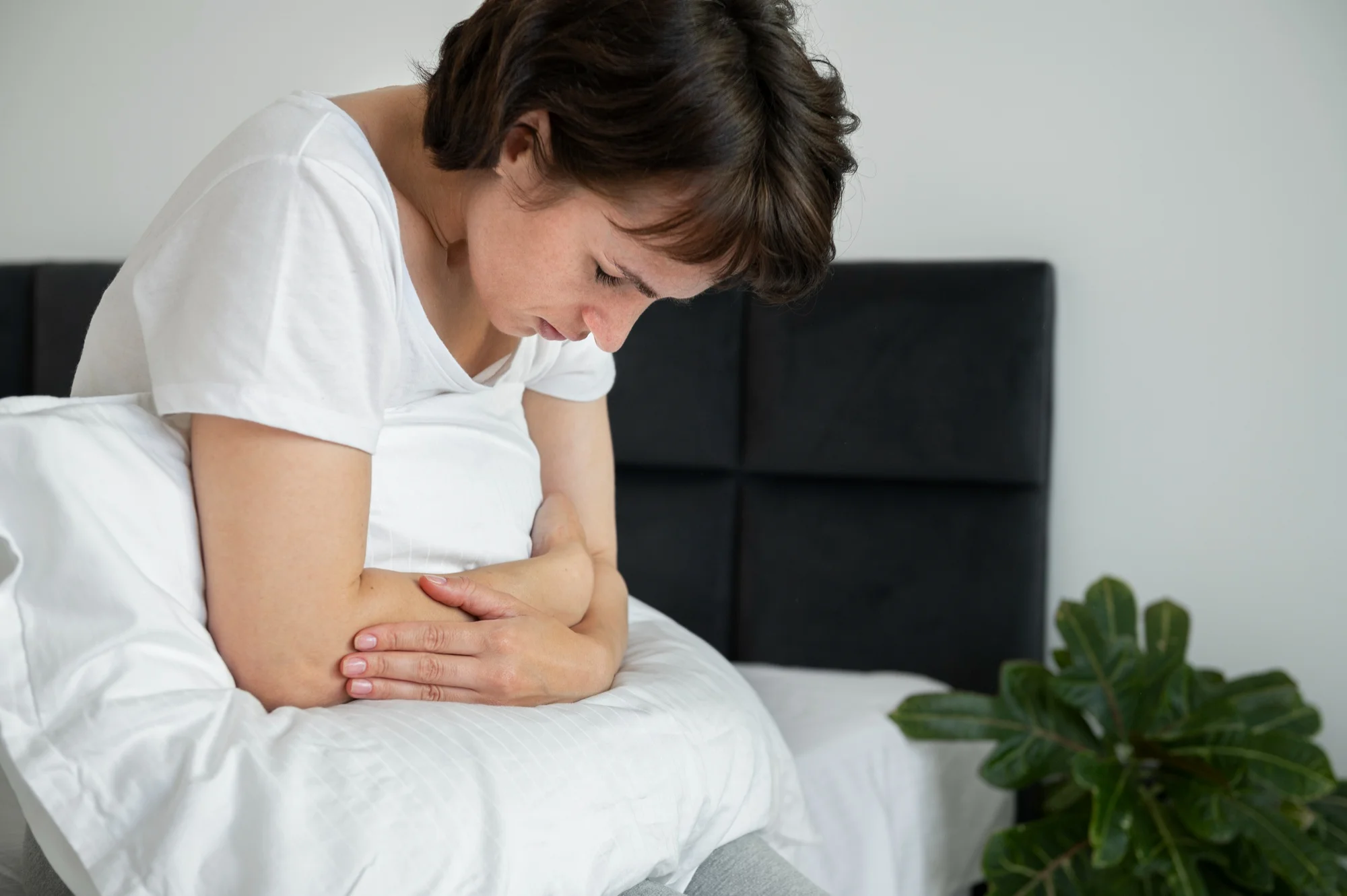
Introduction Menstrual disorders are a common concern affecting women of all ages, disrupting daily life and often signaling underlying health issues. These disorders encompass a wide range of symptoms related to the menstrual cycle, from irregular periods and heavy bleeding to severe pain and mood disturbances. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for menstrual disorders is essential for managing these conditions and improving quality of life.
Types of Menstrual Disorders
- Amenorrhea
- Primary Amenorrhea: This occurs when a girl has not started menstruating by age 16. It can be caused by genetic conditions, hormonal imbalances, or anatomical abnormalities.
- Secondary Amenorrhea: This is when a woman who previously had regular periods stops menstruating for three months or more. Common causes include pregnancy, stress, significant weight loss or gain, and conditions like polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS).
- Dysmenorrhea
- Primary Dysmenorrhea: Refers to common menstrual cramps that occur with no underlying health condition. These cramps are caused by the uterus contracting to shed its lining.
- Secondary Dysmenorrhea: This type of pain is linked to underlying reproductive health issues, such as endometriosis, fibroids, or pelvic inflammatory disease (PID).
- Menorrhagia
- Menorrhagia refers to abnormally heavy or prolonged menstrual bleeding. It can interfere with daily activities and may be caused by hormonal imbalances, uterine fibroids, polyps, or bleeding disorders. In some cases, it may lead to anemia if not managed properly.
- Oligomenorrhea
- This condition is characterized by infrequent menstrual periods, with cycles longer than 35 days. Causes include PCOS, thyroid dysfunction, and excessive exercise or stress.
- Premenstrual Syndrome (PMS) and Premenstrual Dysphoric Disorder (PMDD)
- PMS involves a combination of emotional and physical symptoms that occur in the luteal phase of the menstrual cycle, typically 1-2 weeks before menstruation. Symptoms can include mood swings, bloating, breast tenderness, and fatigue.
- PMDD is a severe form of PMS, with symptoms that can be debilitating, including severe depression, irritability, and anxiety. PMDD often requires more intensive treatment.
Causes of Menstrual Disorders Several factors can contribute to menstrual disorders, including:
- Hormonal Imbalances: Fluctuations in hormones like estrogen and progesterone can disrupt the menstrual cycle, leading to conditions like PCOS, thyroid disorders, and menopause-related changes.
- Structural Problems: Uterine fibroids, polyps, and endometriosis are common causes of abnormal bleeding and pain during menstruation.
- Lifestyle Factors: Stress, excessive exercise, sudden weight changes, and poor nutrition can all affect the regularity and flow of menstrual periods.
- Medications: Certain medications, including hormonal contraceptives, anticoagulants, and some psychiatric drugs, can influence the menstrual cycle.
- Underlying Health Conditions: Chronic conditions such as diabetes, thyroid disorders, and blood clotting disorders can also lead to menstrual irregularities.
Symptoms of Menstrual Disorders The symptoms of menstrual disorders can vary widely depending on the type of disorder. Common symptoms include:
- Irregular or absent periods
- Heavy or prolonged bleeding
- Severe menstrual cramps
- Mood swings, irritability, and anxiety
- Fatigue and low energy
- Bloating and breast tenderness
- Pain during intercourse or bowel movements
Diagnosis Diagnosing menstrual disorders typically involves a combination of medical history, physical exams, and diagnostic tests. A gynecologist may perform the following:
- Pelvic Exam: To check for abnormalities in the reproductive organs.
- Ultrasound: To visualize the uterus, ovaries, and other pelvic organs.
- Blood Tests: To assess hormone levels and detect any underlying conditions like thyroid disorders or anemia.
- Endometrial Biopsy: To examine the uterine lining for abnormal cells or cancer.
- Hysteroscopy: To view the inside of the uterus with a small camera.
Treatment Options Treatment for menstrual disorders depends on the underlying cause and the severity of the symptoms. Common treatment options include:
- Lifestyle Modifications
- Maintaining a healthy diet, regular exercise, and stress management can help regulate the menstrual cycle and alleviate symptoms.
- Medication
- Hormonal Therapy: Birth control pills, hormonal IUDs, and other hormonal treatments can help regulate periods, reduce heavy bleeding, and manage pain.
- Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs): Medications like ibuprofen can relieve menstrual cramps and reduce inflammation.
- Antidepressants: For severe PMS or PMDD, antidepressants such as selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) may be prescribed.
- Surgical Interventions
- Hysterectomy: In severe cases of uterine fibroids, endometriosis, or cancer, a hysterectomy (removal of the uterus) may be necessary.
- Myomectomy: For women with fibroids who wish to preserve fertility, a myomectomy (removal of fibroids) may be performed.
- Endometrial Ablation: This procedure destroys the uterine lining to reduce heavy menstrual bleeding in women who do not plan to have children in the future.
- Alternative Therapies
- Acupuncture, herbal supplements, and dietary changes may also provide relief for some women, although these should be discussed with a healthcare provider to ensure safety and efficacy.
Conclusion Menstrual disorders can significantly impact a woman’s quality of life, but with the right diagnosis and treatment, many of these conditions can be effectively managed. Regular gynecological check-ups, a healthy lifestyle, and open communication with healthcare providers are key to maintaining menstrual health. If you experience any symptoms of a menstrual disorder, it’s important to seek medical advice to identify the cause and explore appropriate treatment options. Early intervention can lead to better outcomes and improved well-being.